| Dry temperature - Wet temperature - Dew temperature - Relative humidity - Specific moisture - Enthalpy - Density - Specific volume - Enthalpy of the air - Sensible Heat - Latent heat - Vapor pressure - Pressure of the saturating vapor - Adiabatic temperature of saturation. |
| _You are in the heading |
|
|
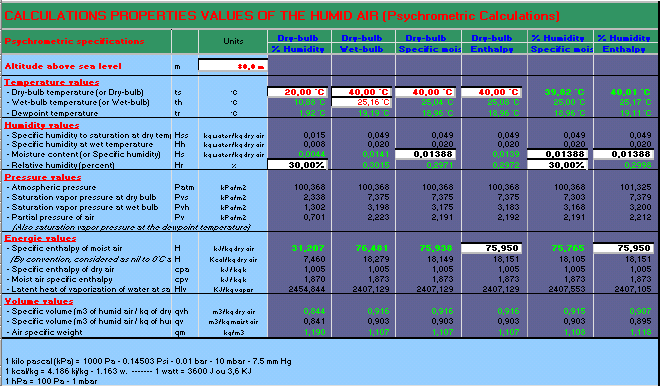
Calculs psychrométriques The program makes it possible according of 2 elements of inputs to know all the other parameters of a state of the humid air, which is to say in function:
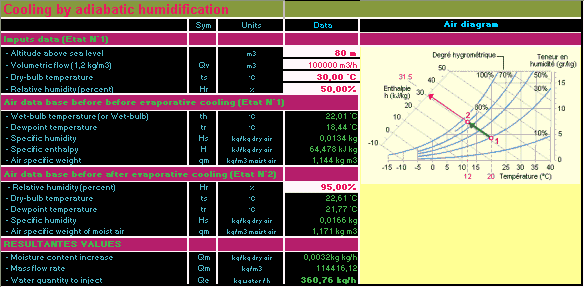
The function of calculation of the temperature of the humid air is done by iteration, i.e. successive approaches. The margin of error can to be near of 0.1°C at most. Cooling by adiabatic humidification Cooling and humidification can be achieved by water spraying
in the air. One calls this "adiabatic process", provided
that there is neither contribution nor withdrawal of heat. This
phenomenon is also known under the name of evaporation cooling.
When the air unsaturated comes in contact with recycled spray
water, there is water evaporation, if the process is adequate,
the air will be saturated. If there is not contribution of heat
during this stage, heat necessary to the evaporation of water
can be provided only by the air, which results with a fall from
temperature from the air and to an increase in the relative
humidity. The total enthalpy of the humid air remains the same
one. This is said "about humidifiers with constant enthalpy ",
such as:
The calculation program makes it possible to carry out psychrometric calculations of the air before vaporization and also the air after cooling adiabatic according to hygrometric rate given.
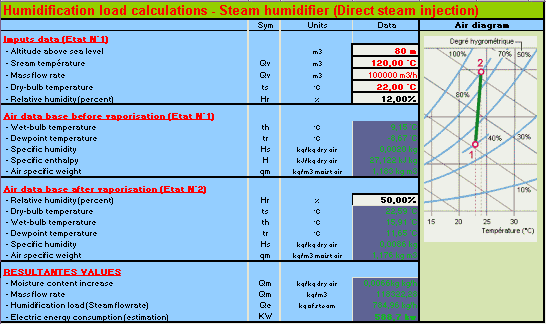
Humidification by steam water injection The steam humidifier is autonomous when it is equipped with an
autonomous vapor generator or not if it must be connected to a network
existing vapor. This process of isothermal humidification involves
an increase in the temperature locally.
By injecting steam water the temperature of the air vairy little.
However to determine with precision the psychrometric characteristics
of the air, it is necessary to carry out the calculation of
this temperature. The calculation programme makes it possible to carry out psychrometric
calculations of the air before vaporization and also that the
air after vaporization of the vapor according to preset rate's
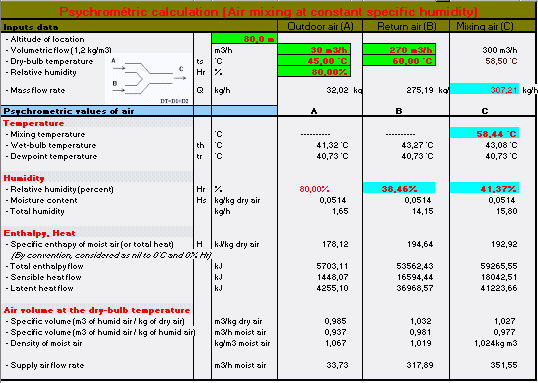
of hygroscopy and of the introduced water vapor. Psychrometric calculation by mixture of air with constant specific moisture
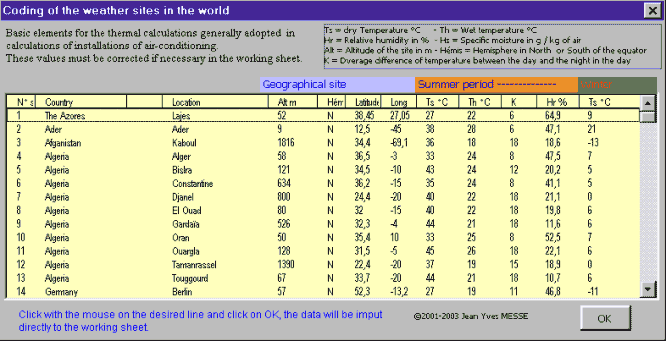
Weather data for thermal calculations In program PYSCHROSI is integrated a library of the weather data defining the climatic parameters adopted in general for the dimensioning of the installations of air-conditioning.
General definitions In air-conditioning, it is of use to work with the mass flow qm
(in kg/s or kg/h), because the volume flow qv (in m³/s or m³/h)
are variable according to the temperature (1 kg of air increases
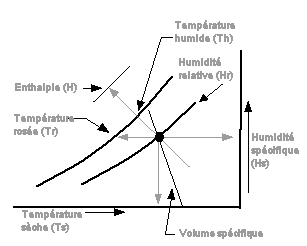
in volume with the rise in temperature). DRY TEMPERATURE in °C - Actual temperature of the humid
air observed using a thermometer or of a temperature gauge. It is
the temperature of the air indicated by a no affected thermometer
by the moisture of air. WET TEMPERATURE in °C - It is the temperature recorded
by a thermometer where the bulb is covered with an impregnated water
wick. The wet temperatures are always lower than the dry temperatures
and the only case where they are identical is with a relative humidity
at 100%. Adiabatic saturation temperature - Temperature to which the humid air can be brought to adiabatic saturation by the evaporation of water, i.e. at the wet temperature (no gain or loss of heat to the environments) DEW TEMPERATURE in °C - It is the temperature from which the water vapor contained in the humid air starts to condense in contact with a cold surface. During a cooling, specific moisture and the partial pressure of the water vapor remain constant. SPECIFIC HUMIDITE or absolute humidity or water content - (Humidity ratio, moisture constant, mixing ratio, gold specific humidity): It is the water mass (liquid, solid, vapor) contained in one kg of dry air. This water weight remains constant when the ambient temperature varies provided that it does not fall below the dew temperature. If the temperature falls below dew point, part of this water mass will condense in the form of droplets on the coldest walls. RELATIVE HUMIDITE in % - It is the ratio of the mass of the water vapor contained in a certain quantity of humid air to the vapor mass which it could contain if it were saturated at the same temperature. To 100%, the air is completely saturated. To 50%, the air contains half of what it could have if it were saturated at the same temperature. When the water content reaches 100% the formation of droplets of liquid occurs on the objects! SPECIFIC VOLUME in m3/kg of air - It is the volume occupied by the weight of one kilogram of dry air in a whole of specific conditions. DENSITY in kg/m3 of humid air: It is the mass of one m3 of humid air. The pressure of the mixture (dry air + water vapor) is equal to the sum of the pressures would have each component if it were alone to occupy the volume of the unit. Therefore in one m3 of humid air, one finds the sum of the masses of components, it is the sum of the density of the dry air and the water vapor, with the partial pressures and indicated temperatures. ENTHALPY - Total energy (heat) contained in the unit weight of the humid air (By convention, regarded as no one at 0°C). The enthalpy includes sensible heat and the latent heat contained in the air. SENSIBLE HEAT and LATENT HEAT - Sensible heat is heat (energy) in the air due to the temperature of air. The latent heat is heat (energy) in the air due to the moisture of air. After this, the air with the same quantity of energy can be dry hot air (high sensible heat) or refreshed humid air (high latent heat) Vapor pressure - It is the pressure partial vapor in the air. This pressure is the same as the saturating vapor pressure at the dew temperature. Saturating vapor pressure - It is the maximum vapor pressure
which the air can support (not supersaturated) at a given temperature.
The saturating vapor pressure increases with the temperature or
loss of heat to the environments) Complementary definitions SHF (Sensitive Heat Factor) - Ratio of sensible heat to total heat By-pass Factor: By-pass Factor is a function of the physical
characteristics of the coil and the operating conditions. It is
considered that it represents the percentage of air which passes
through the coil without undergoing some changes. Psychrometric functions The functions below are used in the working file and can be re-used on other worksheets of this same sorter. These functions are written in Visual BASIC especially for Excel
Atmospheric pressure
in kPa Pressure vapor
in kPa Pressure partial
vapor in kPa Pressure vapor
of saturation in kPa Specific moisture
to saturation in kg / m3 of dry air Specific moisture
in kg / m3 of dry air Specific moisture
in kg / m3 of dry air Relative humidity
in % Dry temperature
(°C) Dry temperature
(°C) according to H and Hs Dew temperature
(°C) Dew temperature
(°C) Enthalpy in Kj/kg
of dry air Enthalpy in Kcal/kg
of dry air Specific heat
of the dry air in kJ / kg K Specific heat
of moisture in kJ / kg K Latent heat of
vaporization at saturation in kJ/kg Density in kg/m3
of humid air Specific volume
in m3 of humid air / kg of dry air Specific volume
in m3 of humid air / kg of humid air Wet temperature
°C Adiabatic temperature (Calculation in adiabatic cooling) Iterative calculation = calculation is done by iteration, i.e.
successive approaches. The margin of error can be at 0.1°C.
at most Last update:
|
Copyright © 2003-2014 - ThermExcel - All Rights Reserved